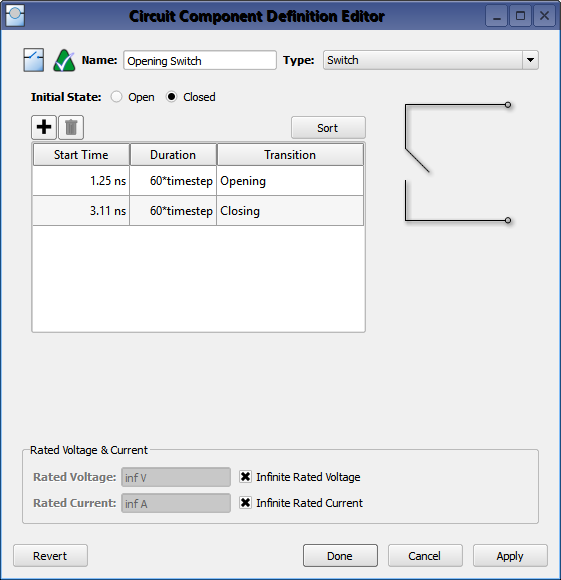
A ![]() Switch circuit component definition is an active component that allows a change in the geometry's configuration during a calculation. It is defined by specifying an initial state—either open or closed—as well as the time at which the transition begins and the duration of time that the action will last.
Switch circuit component definition is an active component that allows a change in the geometry's configuration during a calculation. It is defined by specifying an initial state—either open or closed—as well as the time at which the transition begins and the duration of time that the action will last.
Background
Switches are updated during a finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) simulation by modifying the instantaneous electric field
\begin{equation} E\big|^n = \chi\big|^nE\big|^n \end{equation}where $\chi\big|^n$ represents the state of a switch at timestep, $n$. The electric field at the switch location is first calculated as though the switch were not present. That value is then multiplied by zero or one for a closed or open switch, respectively. Because the initial calculation omits the switch state, the switch's function depends on the material that exists at the mesh location. Given that $E=0$ for perfect electric conductors, a closed switch acts as a wire.
During a transition, a Gaussian function is applied in order to smooth the transition from either zero to one (as a closed switch opens), or one to zero (as an open switch closes). The transition should take place over approximately 60 timesteps in order to reduce the amount of high-frequency transient signals being introduced into the simulation space.
Switches should be used when only time-domain results are of interest. This is because switches violate the assumptions of linear system theory, making it incorrect to apply either a Fourier or discrete Fourier transform to the time-domain results. A simulation containing a switch produces invalid frequency-domain results—including impedances, S-parameters, and steady-state far-zone fields—even if the time-domain results eventually decay to zero. The time-domain results are unaffected, and therefore are valid.