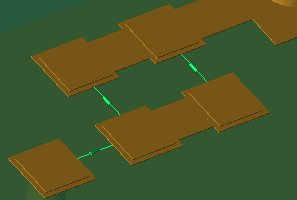
 Circuit Components are discrete components, such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, voltage sources, current sources, switches and diodes. Voltage and current sources are locations at which the electric field is modified by adding an input waveform.
Circuit Components are discrete components, such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, voltage sources, current sources, switches and diodes. Voltage and current sources are locations at which the electric field is modified by adding an input waveform.
A circuit component is always paired with a circuit component definition. The former specifies the component's location in space, and the latter identifies it as a resistor, voltage source, or switch.
Use Cases
Circuit components and their associated definitions support a wide range of use cases:
- A single voltage source exciting a microstrip transmission line that is feeding an antenna.
- Numerous voltage sources with varying phases exciting an antenna array.
- Resistors, capacitors, or inductors providing a matching circuit for an antenna.
- Feeds and passive loads simulating the behavior of MRI coils.
Create and Edit
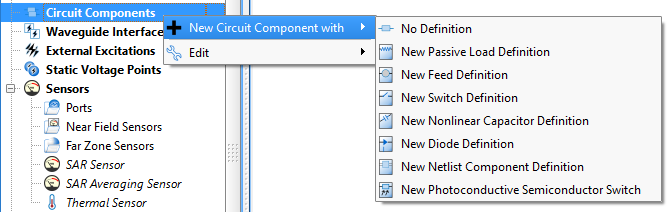
Create a circuit component by right-clicking on Circuit Components in the Project Tree and selecting New Circuit Component with, and then choose from the drop-down menu options to open the editor. Selecting a new definition option adds a definition to the Definitions branch of the Project Tree.
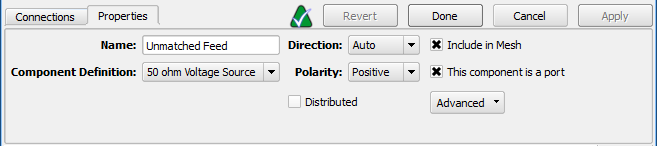
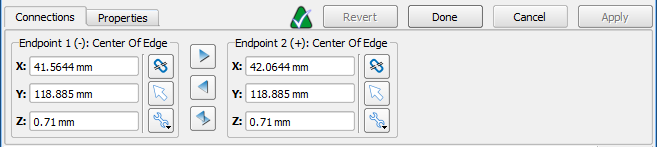
Under the Properties tab, the component's name, direction, and polarity is defined:
- Name: a user-defined descriptor that will be referenced when creating simulations and analyzing results.
- Component Definition: associates electromagnetic properties with the component.
- Direction: orients the component along the selected x-, y-, or z-axis, or allows XF to determine the orientation based on the endpoints when the auto option is selected.
- Polarity: sets the positive or negative value associated with both endpoints.
- Distributed: spreads the component across the width of the trace it is attached to.
- Include in Mesh: includes the component in the mesh.
- This component is a port: assigns the component as a port, prompting XF to add a port sensor at the specified location.
- Advanced: displays additional controls that affect how the computational grid is generated in the vicinity of the component.
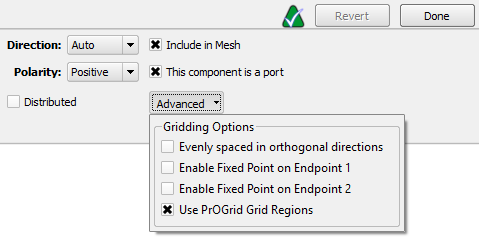
Advanced gridding options can be accessed through the drop-down arrow:
- Evenly spaced in orthogonal directions: applies the same cell size in the two directions perpendicular to the component's axis.
- Enable Fixed Point on Endpoint 1: inserts a fixed point at the circuit component's first endpoint.
- Enable Fixed Point on Endpoint 2: inserts a fixed point at the circuit component's second endpoint.
- Use PrOGrid Grid Regions: applies PrOGrid boundary refinements to reduce grid cell sizes near the circuit component.
Applying the Use PrOGrid Grid Regions setting resolves the distance between the two component endpoints by a minimum of one grid cell and adds boundary refinements on the line defining the circuit component. These refinements reduce cell sizes in directions perpendicular to the circuit component. A circuit component's boundary refinements are determined by both the main grid's Good Conductor Boundary Refinement Ratio and Boundary Refinement Number of Cells values.
Simulate
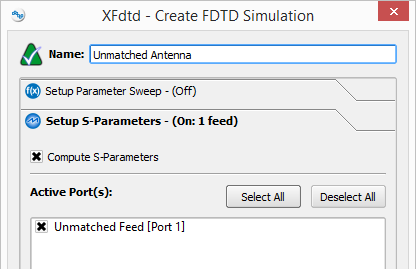
Users can set up a simulation either with or without S-parameters. When S-parameters are enabled and more than one port is selected, the simulation will contain one run for each selected port. In each run, one of the selected ports is active and all other sources are inactive.
When S-parameters are disabled, all ports will be active with the power specified in their circuit component definition.
![]() Circuit Components are discrete components, such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, voltage sources, current sources, switches and diodes. Voltage and current sources are locations at which the electric field is modified by adding an input waveform.
Circuit Components are discrete components, such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, voltage sources, current sources, switches and diodes. Voltage and current sources are locations at which the electric field is modified by adding an input waveform.